Table of Contents
Java Learning Roadmap 2025: My Complete Self-Study Plan (Beginner to Advanced)
Learning Java can feel overwhelming at first. There are countless tutorials, videos, and courses, and most beginners struggle to decide what to learn first and what to skip. I faced the same confusion when I started learning Java.
So, instead of randomly watching videos, I created this Java Learning Roadmap for 2025 — a clear, step-by-step self-study plan that takes you from basic programming logic to advanced Java concepts, with practice and projects along the way.
If you are a beginner, you can follow this roadmap exactly as I’m doing.
Why I Created This Java Roadmap
When I began learning Java, I noticed three major problems:
- Topics were scattered across different platforms
- Many tutorials skipped fundamentals
- There was no clear progression from basics to advanced concepts
I wanted one structured learning path that focuses on:
- Logic building before coding
- Understanding concepts instead of memorizing syntax
- Applying learning through small programs and projects
This roadmap is not copied from a syllabus.
It is a practical learning plan designed to keep me consistent and focused every day.
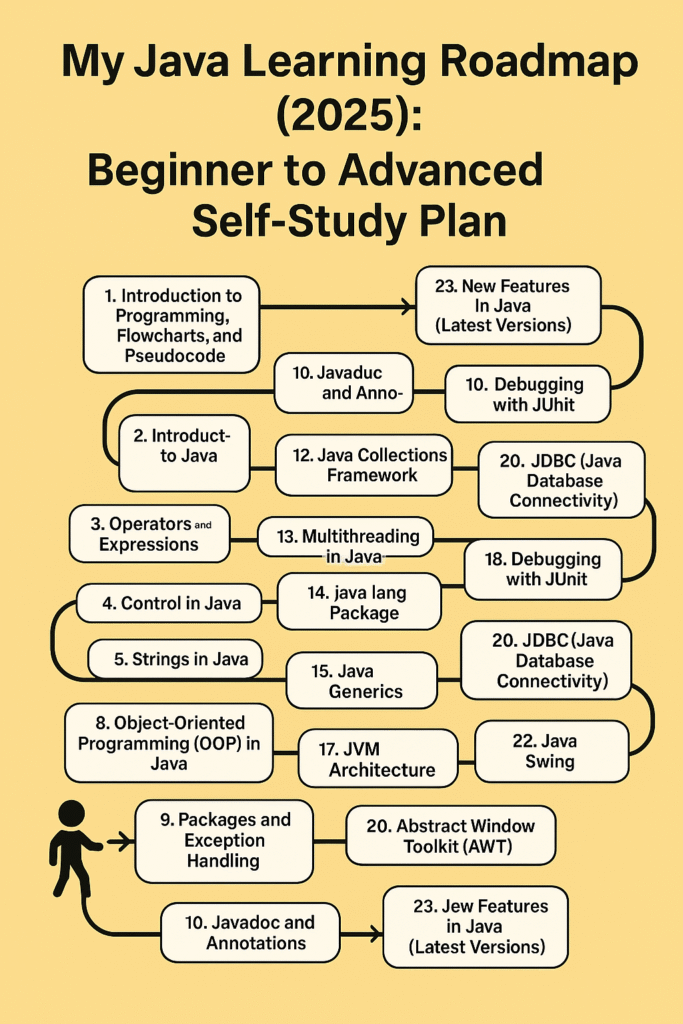
My Step-by-Step Java Learning Roadmap (2025)
1. Programming Basics: Flowcharts & Pseudocode
Before touching Java, I focused on understanding how programs think.
- What is a program?
- How logic flows step by step
- Writing pseudocode before coding
This step helped me avoid confusion later when learning conditions and loops.
2. Introduction to Java
At this stage, I learned:
- Installing JDK and setting up an IDE (IntelliJ / VS Code)
- Difference between JVM, JDK, and JRE
- Writing and running my first Java program
Understanding how Java runs internally made debugging easier later.
3. Operators and Expressions
Here, I practiced:
- Arithmetic, relational, logical, and conditional operators
- Expression evaluation rules
- Writing small programs to test conditions
This topic is crucial for writing correct logic.
4. Control Flow Statements
I learned how Java makes decisions:
- if, else, else-if
- switch-case
- Loops: for, while, do-while
I practiced common problems like number patterns and basic calculations.
5. Methods in Java
Methods helped me write clean and reusable code.
- Method declaration and calling
- Parameters and return values
- Method overloading
- Basic recursion like factorial and Fibonacci
6. Arrays in Java
Arrays taught me how to store multiple values:
- 1D and 2D arrays
- Traversing arrays using loops
- Finding max, min, sum, and searching elements
7. Strings in Java
Strings are used everywhere in Java programs.
- String methods like length(), equals(), substring()
- Difference between String, StringBuilder, and StringBuffer
- Simple string manipulation programs
8. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java
This is one of the most important parts of Java.
I focused on:
- Classes and objects
- Constructors
- Four pillars of OOP:
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Abstraction
I also practiced keywords like this, super, static, and final.
9. Packages and Exception Handling
To write professional code, I learned:
- Creating and using packages
- Handling runtime errors using try-catch
- Custom exceptions and the use of throw and throws
10. JavaDoc and Annotations
I explored:
- Writing JavaDoc comments
- Common annotations like @Override and @Deprecated
This improved my code readability.
11. File I/O in Java
This topic helped me work with files:
- Reading and writing files using FileReader and BufferedReader
- Writing output using FileWriter and PrintWriter
- Creating simple file-based programs
12. Java Collections Framework
Collections made data handling easier:
- List (ArrayList, LinkedList)
- Set (HashSet, TreeSet)
- Map (HashMap, TreeMap)
I used them in small programs like student records.
13. Multithreading in Java
I learned how Java handles multiple tasks:
- Creating threads using Thread and Runnable
- Thread lifecycle
- Synchronization basics
This topic was challenging but very useful.
14. java.lang Package
I studied commonly used classes:
- Object, String, Math, System
- Wrapper classes like Integer and Double
15. Java Generics
Generics helped me write type-safe code:
- Generic classes and methods
- Using generics with collections
16. Lambda Expressions
I learned:
- Functional interfaces
- Writing simple lambda expressions
- Using lambdas for sorting and iteration
17. JVM Architecture
Understanding JVM internals helped me write efficient code:
- Class loading process
- Memory areas (Heap, Stack, Method Area)
- Garbage collection basics
18. Networking with Sockets
I explored basic networking concepts:
- Client-server communication
- Socket and ServerSocket classes
19. Debugging and Testing with JUnit
Testing improved my confidence:
- Writing test cases
- Using assertions
- Debugging logic errors effectively
20. JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
I connected Java with databases:
- MySQL connection
- CRUD operations
- Using PreparedStatement for security
21. AWT and 22. Java Swing
For GUI development, I learned:
- Creating windows, buttons, and forms
- Event handling
- Building small GUI applications
23. New Features in Modern Java
I explored recent Java features:
- var keyword
- Records
- Text Blocks
- Enhanced switch and pattern matching
I referred to the official Java documentation for updates.
Java Projects I Plan to Build
To apply what I learn, I plan to build:
- Console-based ATM system
- File reader and writer utility
- To-do list using ArrayList
- Student record system using JDBC
- GUI calculator using Swing
- Simple chat application using sockets
Projects help convert theory into real understanding.
Recommended Resources to Learn Java Effectively
1. Official Java Documentation (Must-have)
🔗 https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/
Best source for understanding Java features, JVM behavior, and official updates.
2. Oracle Java Tutorials (Beginner-Friendly)
🔗 https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/
Helpful for learning Java fundamentals with structured examples.
3. GeeksforGeeks – Java
🔗 https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/java/
Useful for practicing Java programs and understanding concepts with examples.
4. Baeldung Java Guides (Optional but Excellent)
🔗 https://www.baeldung.com/java-tutorial
High-quality explanations for advanced Java topics and best practices.
How I’m Using This Roadmap
- One topic per day
- Handwritten notes
- Daily practice programs
- Regular revision using mini-projects
If you’re a beginner like me, feel free to use this Java learning roadmap as your daily plan.
Let’s take one step at a time. Perfection isn’t the goal — consistency is.
I’ve also created handwritten notes in PDF format for revision purposes
You May Also Like
If you’re enjoying this beginner-friendly Java series, here are a few of my other helpful posts that you might find useful:
Java Learning Roadmap 2025 – From Zero to Pro
A step-by-step guide to how I plan to learn Java in 2025, perfect for beginners who want a clear and structured learning path.
Aptitude Tricks for Beginners – Easy Mental Math Techniques
Simple and effective tricks for multiplication, LCM, squaring, and cubes. These are especially useful for placement preparation and coding exams.
Types of Nouns in English Grammar – Simple Explanation with Examples
A clear explanation of all types of nouns with examples, helpful for improving communication skills and competitive exam preparation.



Pingback: Aptitude Tricks for Beginners – My Day 1 Journey with Fun Math Shortcuts - Monika's Study Space
Pingback: Java Introduction to Programming: My Exciting Day 1 Journey from Zero to Beginner - Monika's Study Space
Pingback: Data Cleaning with Titanic Dataset: Top 7 Preprocessing Tips to Master ML - Monika's Study Space
Pingback: Front-End Developer Intern – Remote Internship at Unified Mentor (₹7,500–₹15,000 Stipend + Certificate) - Monika's Study Space