Table of Contents
Java Introduction to Programming: My Day 1 Learning Journey as a Beginner
Today marks the beginning of my journey into the world of Java programming. As a complete beginner, I spent Day 1 building a strong foundation in problem-solving and programming logic before writing a single line of Java code. In this blog post, I’ll walk you through everything I learned today—from understanding algorithms to solving simple logical problems.
What is Java and Why Start Here?
Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language used to build web applications, mobile apps, games, and more. Its portability, security, and widespread use make it a strong choice for beginners and professionals alike. But before learning Java syntax, I took time to understand how programming works at a logical level.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Here are some key concepts I learned on Day 1:
1. What is an Algorithm?
An algorithm is a set of instructions used to solve a problem. It’s not specific to any language—it’s just logical steps written in a structured way.
Example: Algorithm to Make Tea
- Step 1: Boil water
- Step 2: Add tea powder
- Step 3: Add sugar
- Step 4: Add milk
- Step 5: Boil the mixture
- Step 6: Filter the tea
- Step 7: Serve hot
2. Programming vs Coding
- Programming is about planning, designing logic, and solving problems.
- Coding is the implementation of that logic using a programming language like Java.
3. Types of Programming Languages
- Low-Level Language: Machine-level instructions (e.g., Assembly)
- Middle-Level Language: Closer to both machine and human languages (e.g., C)
- High-Level Language: Easy to read and write (e.g., Java, Python)
What is Pseudocode?
Pseudocode is a simplified version of programming logic written in plain English. It is used to plan the steps of a program before actual coding.
Example: Pseudocode to Add Two Numbers
- Step 1: Start
- Step 2: Read two numbers: num1 and num2
- Step 3: Add the numbers and store in a variable: sum = num1 + num2
- Step 4: Display the result
- Step 5: Stop
Logic Building Exercises
To apply the concepts I learned, I solved some basic problems using pseudocode and flowcharts.
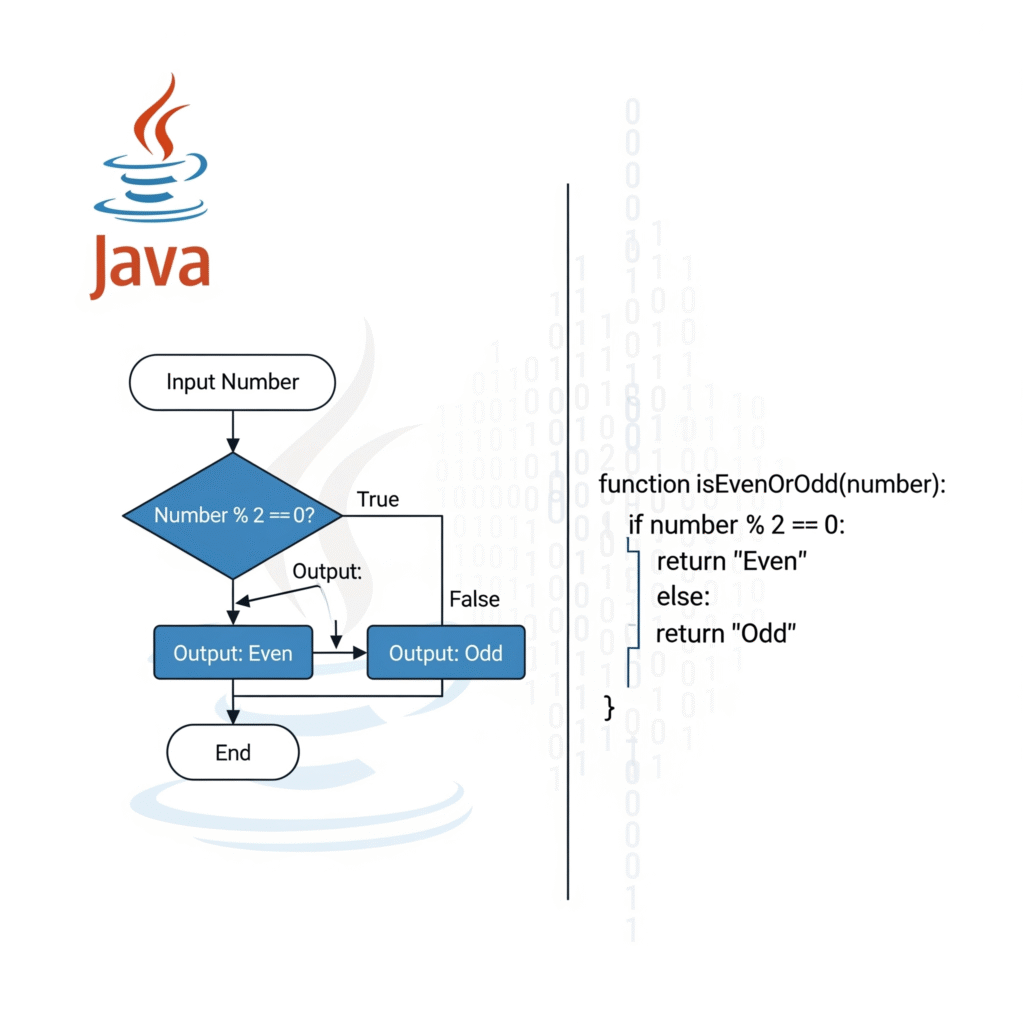
Problem 1: Check Whether a Number is Even or Odd
Algorithm:
- Step 1: Start
- Step 2: Input a number
- Step 3: Divide the number by 2
- Step 4: If the remainder is 0, the number is even
- Step 5: Else, the number is odd
- Step 6: Stop
Problem 2: Print Numbers from 1 to 10
Algorithm:
- Step 1: Start
- Step 2: Initialize a variable i = 1
- Step 3: Repeat while i <= 10
- Step 4: Print i
- Step 5: Increment i by 1
- Step 6: Stop
Problem 3: Find the Greatest of Three Numbers
Algorithm:
- Step 1: Start
- Step 2: Input three numbers a, b, and c
- Step 3: If a > b and a > c, then a is the greatest
- Step 4: Else if b > c, then b is the greatest
- Step 5: Else, c is the greatest
- Step 6: Stop
Problem 4: Check Whether a Number is Prime
Algorithm:
- Step 1: Start
- Step 2: Input a number n
- Step 3: Set a flag = 0
- Step 4: Loop from i = 2 to n/2
- Step 5: If n % i == 0, set flag = 1 and break
- Step 6: If flag == 0, number is prime
- Step 7: Else, number is not prime
- Step 8: Stop
Problem 5: Calculate Factorial of a Number
Algorithm:
- Step 1: Start
- Step 2: Input a number n
- Step 3: Set result = 1
- Step 4: Loop from i = 1 to n
- Step 5: Multiply result by i
- Step 6: After the loop, print result
- Step 7: Stop
Introduction to Flowcharts
A flowchart is a visual representation of an algorithm. It uses arrows, decision boxes, and processes to clearly represent the logic. I created simple flowcharts for problems like even/odd checking and printing numbers from 1 to 10.
Practice Questions from Day 1
Here are some problems I solved using algorithms and pseudocode:
- Find the greatest of three numbers
- Check whether a number is prime or not
- Calculate the factorial of a number
- Print numbers from 1 to 10
- Add two numbers
- Create an algorithm for making tea and more
Related Learning Keywords and Topics
To help you explore more on Java and beginner programming, here are some related keywords and topics covered in this blog post:
- Java introduction to programming
- Learn Java for beginners
- Java basics for students
- What is an algorithm in programming
- Difference between coding and programming
- Pseudocode examples in Java
- Java logic building exercises
- How to write flowcharts in programming
- Java Day 1 problems and solutions
- Java for absolute beginners
- Real-life algorithm examples
- Low-level vs high-level language
- Java pseudocode examples
- Java practice questions for beginners
These terms not only reflect what I learned on Day 1 but also serve as helpful pointers if you’re exploring similar topics.
You May Also Like
If you’re enjoying this beginner-friendly Java series, here are a few of my other helpful posts that you might find useful:
- Java Learning Roadmap 2025 – From Zero to Pro
A step-by-step guide to how I plan to learn Java in 2025, perfect for beginners like me. - Aptitude Tricks for Beginners – Easy Mental Math Techniques
Quick tricks for multiplication, LCM, squaring, and cubes — useful for placement and coding exams. - Types of Nouns in English Grammar – Simple Explanation with Examples
Learn all types of nouns clearly with examples — great for communication skills and competitive exams.
Java is a popular high-level programming language widely used in application development.
Learn more on the official Java website:
https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/
My Handwritten Notes
As part of my learning, I created 30 pages of handwritten notes covering all the topics from Day 1: algorithms, pseudocode, flowcharts, logic building, and practice problems. These notes helped me revise better and understand things visually.
You can view or download them below:
Conclusion
Day 1 of my Java learning journey was not about writing code—it was about understanding how to think like a programmer. I learned how important logic, algorithms, and structured thinking are before starting with syntax. With these foundations clear, I’m now ready to dive into actual Java programming from Day 2.

Pingback: Data Cleaning with Titanic Dataset: Top 7 Preprocessing Tips to Master ML - Monika's Study Space