Table of Contents
Introduction: Why Everyone Talks About APIs
What is an API?
Have you ever booked a cab, checked the weather, or logged into a new app using your Google account? If yes, you’ve already interacted with an API — even if you didn’t realize it.
APIs, or Application Programming Interfaces, are the unsung heroes of the digital world. They quietly connect your favorite apps and devices behind the scenes — making sure your food order reaches the restaurant, your payment goes through securely, and your map updates in real time.
Think of APIs as friendly digital messengers that allow different software systems to talk, share data, and work together — seamlessly. Without APIs, most of the online experiences we take for granted wouldn’t even exist.
In this guide, we’ll break down what an API really is, how it works (in simple terms), explore real-world examples, and even show you how to test one yourself — so by the end, you’ll not only understand APIs but actually appreciate how magical they are.
From your smartwatch syncing your heart rate to your phone to a travel app showing real-time flight updates, APIs make it happen.
In this blog, you’ll learn:
- What is an API
- How APIs work
- Types of APIs
- Real-world examples
- How to use and test an API step-by-step
Let’s dive in
What Does API Stand For?
API stands for Application Programming Interface.
Let’s break that down simply:
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Application | Any software program (like Instagram or a weather app) |
| Programming | The process of writing instructions for computers |
| Interface | A way for two systems to communicate and exchange information |
So, an API is a set of rules that allows one piece of software to communicate with another — safely and efficiently.
The Restaurant Analogy
Imagine you’re sitting in a restaurant:
- You (the user) are hungry and want food.
- The kitchen is the system that prepares your food (data or service).
- You don’t go to the kitchen yourself — you call the waiter.
The waiter takes your order, tells the kitchen, and brings the meal back to you.
In this analogy:
- You = User or Application
- Waiter = API
- Kitchen = Server or Database
So, the API acts as a bridge between your request and the system’s response.
That’s exactly how it works in software systems.
How Does an API Work?
APIs work through a request–response cycle using the internet.
Step-by-Step:
- Client (Request):
An app sends a request to the API asking for information.
Example: A weather app requests “current temperature of London.” - API (Middleman):
The API forwards the request to the appropriate server. - Server (Response):
The server processes the request and sends the result back. - Client (Display):
The app receives the response and shows it to the user.
Example:
Request: https://api.weather.com/current?city=London
Response: { "temperature": 22, "condition": "Sunny" }
Your app simply displays “22°C, Sunny” — all thanks to an API working behind the scenes.
Why Are APIs Important?
APIs are the backbone of modern technology. Without them, most apps wouldn’t function.
Here’s why they’re so valuable:
- Connectivity: Connects different software easily (e.g., Instagram to Facebook).
- Automation: Reduces manual work by automating data flow.
- Innovation: Developers can build new apps using existing services.
- Security: APIs provide controlled access to data.
- Scalability: Helps systems grow by adding new features without rebuilding everything.
Types of APIs
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Open APIs (Public APIs) | Available for everyone to use | OpenWeather API |
| Internal APIs (Private) | Used only within an organization | Company HR systems |
| Partner APIs | Shared between business partners | Payment gateway integrations |
| Composite APIs | Combine multiple data sources | Dashboard fetching multiple stats |
Common Web API Types
1. REST API (Representational State Transfer)
- Most popular API type
- Uses HTTP methods: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE
- Data sent in JSON format
- Example:
GET https://api.github.com/users/octocat
2. SOAP API (Simple Object Access Protocol)
- Uses XML
- Highly secure but more complex
- Used in banking and enterprise apps
3. GraphQL API
- Created by Facebook
- Lets clients request specific data only — faster and efficient.
4. gRPC
- Uses binary data — faster than JSON.
- Used in modern microservices systems.
Common HTTP Methods in APIs
| Method | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| GET | Retrieve data | Get all users |
| POST | Send new data | Add a comment |
| PUT | Update existing data | Edit profile |
| DELETE | Remove data | Delete a product |
Example:
GET https://api.example.com/users
POST https://api.example.com/users
Real-Life Examples
| API | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Google Maps API | Displays maps and routes in apps like Uber or Swiggy |
| Weather API | Provides real-time forecasts |
| Payment Gateway API (Razorpay/Paytm) | Enables secure online payments |
| Twitter API | Allows developers to read and post tweets |
| ChatGPT API | Lets developers build AI chatbots and assistants |
Example: Fetching Data Using an API (in JavaScript)
fetch("https://api.coindesk.com/v1/bpi/currentprice.json")
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
console.log("Bitcoin Price in USD:", data.bpi.USD.rate);
})
.catch(error => console.error("Error:", error));
This code fetches Bitcoin’s live price from CoinDesk’s API and prints it to the console.
How to Start Using and Testing APIs
Now that you understand what APIs are, let’s see how to use and test one yourself.
🔹 Step 1: Find a Free Public API
Here are some beginner-friendly APIs you can try:
| API | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| OpenWeatherMap | Weather data and forecasts | https://openweathermap.org/api |
| The Dog API | Random dog images | https://thedogapi.com |
| JSONPlaceholder | Fake API for learning | https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com |
| CoinDesk API | Bitcoin price tracker | https://developers.coindesk.com/ |
| GitHub API | Explore GitHub data | https://api.github.com |
🔹 Step 2: Test an API in Your Browser
Try typing this URL in your browser:https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users
You’ll see something like:
[
{ "id": 1, "name": "Leanne Graham", "email": "leanne@example.com" },
{ "id": 2, "name": "Ervin Howell", "email": "ervin@example.com" }
]
That’s your API response in JSON format!
🔹 Step 3: Use Postman to Test APIs Easily
What is Postman?
Postman is a tool used to test APIs without writing code.
Download or Use Online:
- Desktop: https://www.postman.com/downloads/
- Online: https://web.postman.co
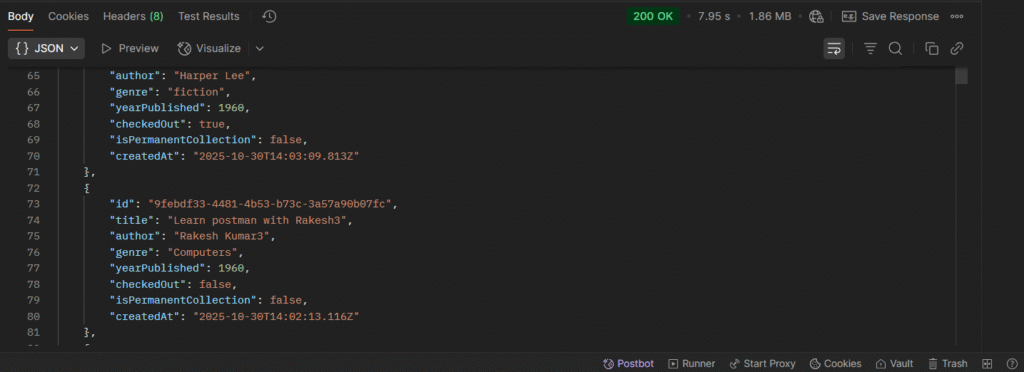
How to Test an API in Postman:
- Open Postman
- Choose
GETmethod - Enter the API URL, for example:
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts - Click Send
- You’ll see the response data below
- Status
200 OK= Success
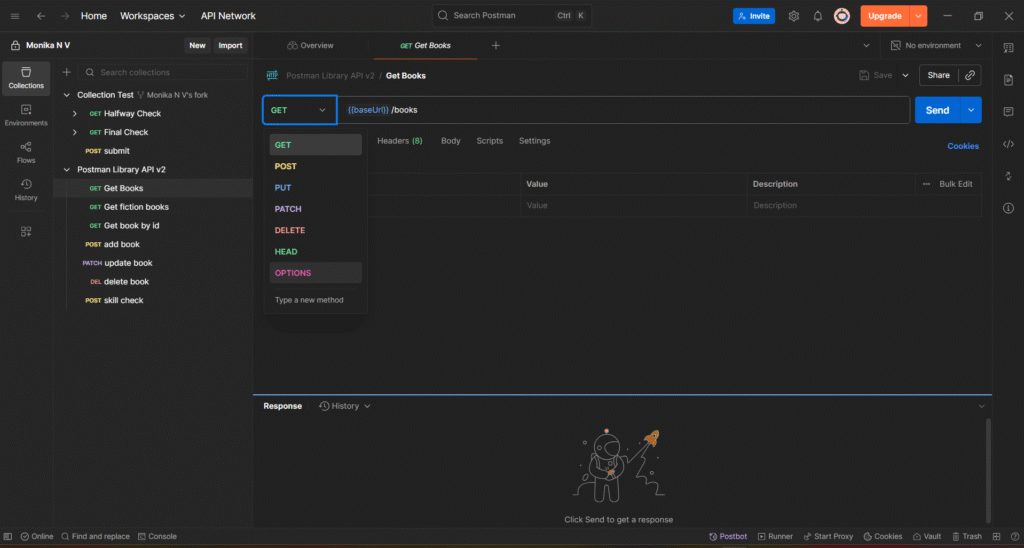
Try Sending Data (POST)
- Choose POST
- Go to the Body tab → select raw → choose JSON
- Enter:
{ "title": "Hello API", "body": "My first API test!", "userId": 1 } - Click Send
- You’ll see a success response:
{ "id": 101, "title": "Hello API", "body": "My first API test!", "userId": 1 }
Congratulations! You just made your first API request!
🔹 Step 4: APIs That Need Keys
Some APIs (like Google Maps, OpenWeather) need an API key for authentication.
How to get one:
- Register on the API provider’s website.
- Generate your free API key.
- Add it to your request like this:
https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q=London&appid=YOUR_API_KEY
This ensures your usage is tracked and secure.
🔹 Step 5: Explore API Marketplaces
If you want to try more APIs, check out these websites:
| Platform | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| RapidAPI Hub | 1000+ APIs for free or paid use | https://rapidapi.com/hub |
| Public APIs List | Curated open APIs by category | https://public-apis.io |
| API Ninjas | Fun APIs like quotes, jokes, and weather | https://api-ninjas.com |
| Postman API Network | Explore and test APIs directly | https://www.postman.com/explore |
Bonus: Test APIs in Code
Python Example:
import requests
response = requests.get("https://api.github.com/users/octocat")
data = response.json()
print("GitHub User:", data["login"])
print("Profile URL:", data["html_url"])
JavaScript Example:
fetch("https://api.github.com/users/octocat")
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => console.log(data))
.catch(err => console.error(err));
Fun APIs to Try for Practice
| API | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Dog API | Shows random dog photos |
| CoinDesk API | Bitcoin price updates |
| OpenWeather API | Weather by city |
| ChatGPT API | Create your own chatbot |
| Spotify API | Access playlists and tracks |
Quick Summary: How to Start and Test an API
| Step | Action | Tool/Link |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Find a free API | https://public-apis.io |
| 2 | Try in browser | Use JSONPlaceholder |
| 3 | Test in Postman | https://www.postman.com |
| 4 | Add API key if needed | From provider |
| 5 | Integrate in code | Python or JavaScript |
API Security Basics
APIs often handle sensitive data, so they use security features like:
- API Keys: Identify who’s using the API
- OAuth Tokens: Secure user logins (used by Google/Facebook)
- HTTPS: Encrypts communication
- Rate Limiting: Prevents abuse or overload
How Developers Create APIs
- Design: Define what data the API should offer.
- Build: Use frameworks like Flask, Express, or Spring Boot.
- Test: Check using Postman or automated scripts.
- Deploy: Host on AWS, Azure, or Render.
- Document: Use Swagger or Notion for documentation.
Future of APIs
- AI-Powered APIs (like ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude) are rising fast.
- Serverless APIs simplify cloud deployment.
- API-first development — companies design APIs before building apps.
APIs are no longer just tools — they’re the foundation of modern software.
Conclusion
So, what is an API?
An API is a bridge that connects software systems — enabling them to share data, automate tasks, and create incredible digital experiences.
From ordering food to using AI chatbots, APIs power the digital world you use every day.
Start exploring free APIs, test them in Postman, and soon you’ll be building your own — step by step!
You May Also Like
If you found this blog interesting, you might enjoy exploring more stories, tips, and insights in our